
Key takeaways
A PCV2 vaccine containing two genotypes (PCV2a and PCV2b) provides broad, antigenic coverage against evolving PCV2 viruses in addition to the predicted protection against PCV2d.
T cells are key mediators of the PCV2 cell-mediated immune response and are most effectively induced by both vaccine antigens that contain relevant T cell epitopes and vaccine adjuvants that promote cell-mediated immunity.
T cell epitopes can be predicted and used to select vaccines with the most T cell epitope coverage common to field strains.
Immunologists at Zoetis were confident that a porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2) vaccine with two genotypes (PCV2a and PCV2b) would provide the broadest range of coverage against evolving PCV2 viruses in US swine herds, including cross protection against the leading genotype PCV2d.
To see if they were on the right track, they collaborated with EpiVax, an informatics and immunology biotechnology company, that develops computational immunology tools.
An epitope is part of an antigen that is recognized by the immune system, specifically by immune cells — including lymphocytes such as T cells. T cells are essential for killing infected host cells (including PCV2-infected cells) and for the development of an effective antibody response. Using a tool called EpiCC to identify and analyze T cell epitopes, EpiVax and Zoetis scientists could plot the predicted immune coverage of different vaccines against PCV2a, PCV2b and PCV2d, which are the most prevalent genotypes affecting US herds, as well as other, less common genotypes such as PCV2e.
Evolving field strains
“Through this computer model, we determined that combining PCV2a and PCV2b in one vaccine could provide considerably more coverage against the evolving field strains of the virus than traditional PCV2 vaccines with only one genotype,” explained Meggan Bandrick, DVM, PhD, Director, Global Biologics, Zoetis.1
“With this technology, we could predict what the pig’s immune system would learn from the vaccine and what PCV2 epitopes it would recognize. From there we could make predictions on vaccine performance against various strains of the virus.”
To make this work, Zoetis obtained sequences from 161 field strains of PCV2 from GenBank, a voluntary repository of global sequences, and provided them to EpiVax for the analysis.
The strains were selected to broadly represent the different PCV2 genotypes found globally. “We looked at 161 strains because there’s a lot of diversity in PCV2 and it continues to evolve,” Bandrick added.
Predicting responses
EpiVax used the EpiCC computational method to predict how swine immune cells bind and present T cell epitopes to their own T cells— in this case, over 800,000 different PCV2 epitopes were predicted. When the T cells recognize the epitope, either from a pathogen or vaccine antigen, an immune response develops.
“EpiCC takes the antigen-binding regions of swine immune cells (cells that display or present epitopes to T cells), predicted from the swine-genome sequence, and compares that to the epitopes, predicted binding regions, on vaccine strains and on field strains,” Bandrick explained.
“Based on this, we can determine how the vaccine is going to convey information to the pig’s immune system so that the vaccine confers protection not only to the vaccine strains but also to field strains.”
Radar plot
Three commercial vaccines were used in the analysis: Fostera® Gold PCV MH (PCV2a plus PCV2b); Fostera® PCV MH (PCV2a only); and a vaccine made with a baculovirus-expressed PCV2a antigen. All vaccines contain Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae bacterin.
A radar plot (Figure 1) shows the results. The field strains are grouped together by genotype and identified on the perimeter of the plot. Each of the 161 PCV2 field strains in the analysis is represented by a single line running from the center to the perimeter. The three jagged starburst patterns inside the radar plot represent how similar the vaccine’s T cell epitopes are compared to that of the 161 field strains.
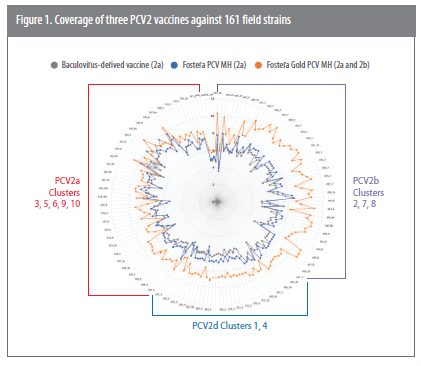
“Note that the amount of T cell epitope overlap, or the number of epitopes the vaccine and field viruses have in common, indicating immune coverage, increases going from the center of the circle to the perimeter,” Bandrick said. “The bigger the circle, or closer to the perimeter it is, the greater the coverage the vaccine virus provides against the field strains.”
The orange line representing Fostera Gold PCV MH covers a significantly broader range than either the gray (baculovirus-derived PCV2a) or the blue (Fostera PCV MH) lines, she added.
“In the vast majority of the cases, we found a significant improvement in coverage from having both PCV2a and PCV2b in the vaccine compared to just having PCV2a,” reported Dennis L. Foss, DVM, PhD, research director, Zoetis. “The PCV2b and PCV2d viruses are more closely related to each other than to the PCV2a viruses. Targeting the b-d cluster with a PCV2b vaccine makes sense and is supported by the EpiCC analysis.”
“We expect a strong correlation between pig immune response to these field-circulating strains and the coverage of the vaccine used,” Bandrick added. “The broader coverage of Fostera Gold PCV MH is important — not just for swine herds today, but also as the PCV2 virus continues to evolve.”
Role of the adjuvant
“Why one vaccine induces stronger cell-mediated immunity (CMI) than another is largely due to the vaccine’s adjuvant — the substance added to vaccines to boost the immune response,” Bandrick stated.
The robust antibody response as well as a strong cell-mediated response is a product of the adjuvant MetaStim which is used in Fostera® Gold PCV MH. “Adjuvants are the instruction manual for the immune system,” said Foss. They play an important role in determining the type of immunity activated. When properly paired with vaccines, adjuvants can steer the animal’s response toward the best, most effective type of immunity for a given pathogen. In a natural infection, the innate immune system recognizes the pathogen (via “molecular patterns”) or some effect of the pathogen (cell damage or death) and signals the immune system to respond appropriately.2 During the development stage of Fostera Gold PCV MH, several adjuvants were evaluated. MetaStim* was found to provide the best balance of humoral and cellular immunity against PCV2.3
(*MetaStim is an oil-in-water emulsion with an oil content of less than 1% by volume. It provides a strong immune response with minimal adverse reactivity.3 Injection site reactions are rare and negligible.)4
References
- Data on file, Study Report Zoetis WO1, EpiCC PCV2 Analysis, Zoetis LLC.
- Pulendran B, S Arunachalam P, O’Hagan DT. Emerging concepts in the science of vaccine adjuvants. Nature reviews. Drug discovery. 2021;20:454-475.
- Venegas-Vargas C, Taylor LP, Foss DL, Godbee TK, Philip R, Bandrick M. Cellular and humoral immunity following vaccination with two different PCV2 vaccines (containing PCV2a or PCV2a/PCV2b) and challenge with virulent PCV2d. Vaccine. 2021;39:5615-5625.
- Data on file, Study Report No. B921R-US-16-609, Zoetis LLC.





